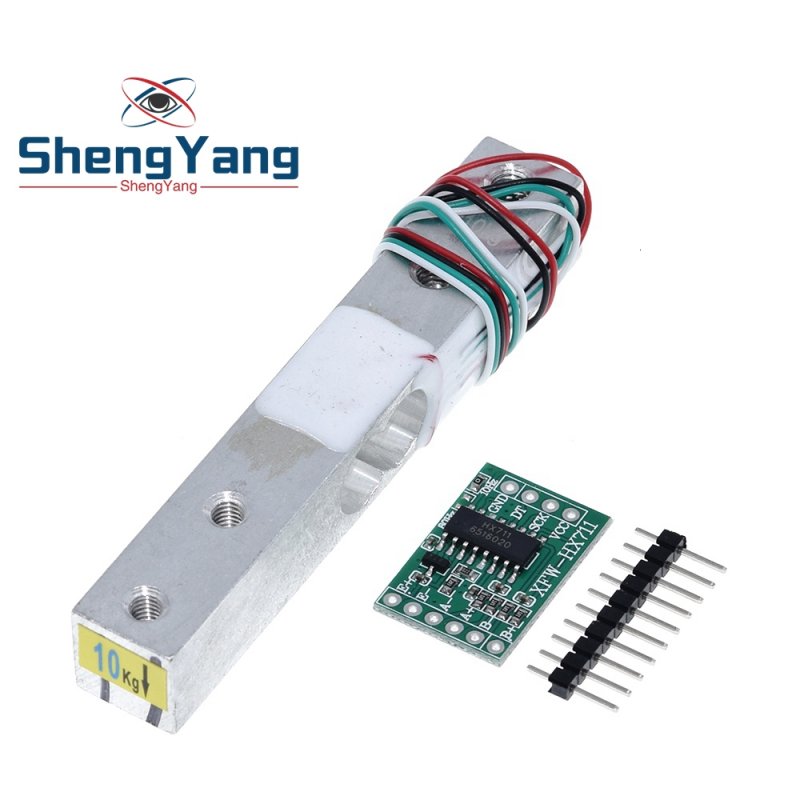
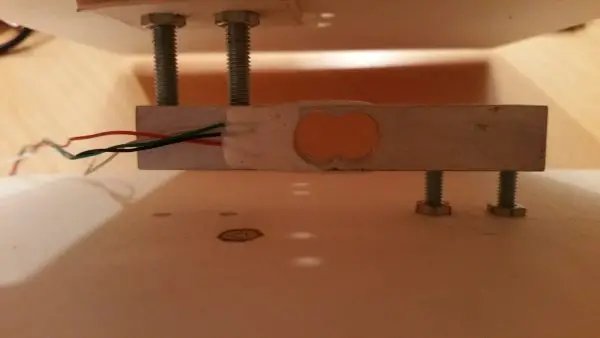
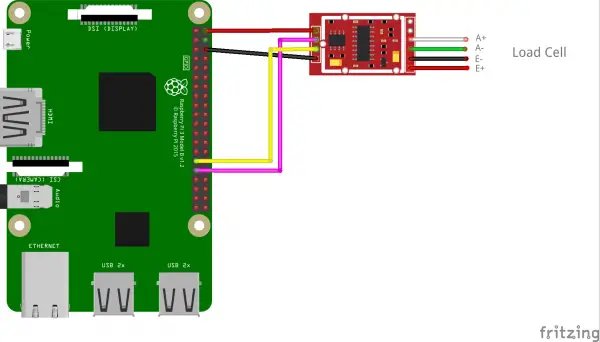
#
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
import threading
class HX711:
def __init__(self, dout, pd_sck, gain=128):
self.PD_SCK = pd_sck
self.DOUT = dout
# Mutex for reading from the HX711, in case multiple threads in client
# software try to access get values from the class at the same time.
self.readLock = threading.Lock()
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(self.PD_SCK, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(self.DOUT, GPIO.IN)
self.GAIN = 0
# The value returned by the hx711 that corresponds to your reference
# unit AFTER dividing by the SCALE.
self.REFERENCE_UNIT = 1
self.REFERENCE_UNIT_B = 1
self.OFFSET = 1
self.OFFSET_B = 1
self.lastVal = int(0)
self.DEBUG_PRINTING = False
self.byte_format = 'MSB'
self.bit_format = 'MSB'
self.set_gain(gain)
# Think about whether this is necessary.
time.sleep(1)
def convertFromTwosComplement24bit(self, inputValue):
return -(inputValue & 0x800000) + (inputValue & 0x7fffff)
def is_ready(self):
return GPIO.input(self.DOUT) == 0
def set_gain(self, gain):
if gain is 128:
self.GAIN = 1
elif gain is 64:
self.GAIN = 3
elif gain is 32:
self.GAIN = 2
GPIO.output(self.PD_SCK, False)
# Read out a set of raw bytes and throw it away.
self.readRawBytes()
def get_gain(self):
if self.GAIN == 1:
return 128
if self.GAIN == 3:
return 64
if self.GAIN == 2:
return 32
# Shouldn't get here.
return 0
def readNextBit(self):
# Clock HX711 Digital Serial Clock (PD_SCK). DOUT will be
# ready 1us after PD_SCK rising edge, so we sample after
# lowering PD_SCL, when we know DOUT will be stable.
GPIO.output(self.PD_SCK, True)
GPIO.output(self.PD_SCK, False)
value = GPIO.input(self.DOUT)
# Convert Boolean to int and return it.
return int(value)
def readNextByte(self):
byteValue = 0
# Read bits and build the byte from top, or bottom, depending
# on whether we are in MSB or LSB bit mode.
for x in range(8):
if self.bit_format == 'MSB':
byteValue <<= 1
byteValue |= self.readNextBit()
else:
byteValue >>= 1
byteValue |= self.readNextBit() * 0x80
# Return the packed byte.
return byteValue
def readRawBytes(self):
# Wait for and get the Read Lock, incase another thread is already
# driving the HX711 serial interface.
self.readLock.acquire()
# Wait until HX711 is ready for us to read a sample.
while not self.is_ready():
pass
# Read three bytes of data from the HX711.
firstByte = self.readNextByte()
secondByte = self.readNextByte()
thirdByte = self.readNextByte()
# HX711 Channel and gain factor are set by number of bits read
# after 24 data bits.
for i in range(self.GAIN):
# Clock a bit out of the HX711 and throw it away.
self.readNextBit()
# Release the Read Lock, now that we've finished driving the HX711
# serial interface.
self.readLock.release()
# Depending on how we're configured, return an orderd list of raw byte
# values.
if self.byte_format == 'LSB':
return [thirdByte, secondByte, firstByte]
else:
return [firstByte, secondByte, thirdByte]
def read_long(self):
# Get a sample from the HX711 in the form of raw bytes.
dataBytes = self.readRawBytes()
if self.DEBUG_PRINTING:
print(dataBytes,)
# Join the raw bytes into a single 24bit 2s complement value.
twosComplementValue = ((dataBytes[0] << 16) |
(dataBytes[1] << 8) |
dataBytes[2])
if self.DEBUG_PRINTING:
print("Twos: 0x%06x" % twosComplementValue)
# Convert from 24bit twos-complement to a signed value.
signedIntValue = self.convertFromTwosComplement24bit(twosComplementValue)
# Record the latest sample value we've read.
self.lastVal = signedIntValue
# Return the sample value we've read from the HX711.
return int(signedIntValue)
def read_average(self, times=3):
# Make sure we've been asked to take a rational amount of samples.
if times <= 0:
raise ValueError("HX711()::read_average(): times must >= 1!!")
# If we're only average across one value, just read it and return it.
if times == 1:
return self.read_long()
# If we're averaging across a low amount of values, just take the
# median.
if times < 5:
return self.read_median(times)
# If we're taking a lot of samples, we'll collect them in a list, remove
# the outliers, then take the mean of the remaining set.
valueList = []
for x in range(times):
valueList += [self.read_long()]
valueList.sort()
# We'll be trimming 20% of outlier samples from top and bottom of collected set.
trimAmount = int(len(valueList) * 0.2)
# Trim the edge case values.
valueList = valueList[trimAmount:-trimAmount]
# Return the mean of remaining samples.
return sum(valueList) / len(valueList)
# A median-based read method, might help when getting random value spikes
# for unknown or CPU-related reasons
def read_median(self, times=3):
if times <= 0:
raise ValueError("HX711::read_median(): times must be greater than zero!")
# If times == 1, just return a single reading.
if times == 1:
return self.read_long()
valueList = []
for x in range(times):
valueList += [self.read_long()]
valueList.sort()
# If times is odd we can just take the centre value.
if (times & 0x1) == 0x1:
return valueList[len(valueList) // 2]
else:
# If times is even we have to take the arithmetic mean of
# the two middle values.
midpoint = len(valueList) / 2
return sum(valueList[midpoint:midpoint+2]) / 2.0
# Compatibility function, uses channel A version
def get_value(self, times=3):
return self.get_value_A(times)
def get_value_A(self, times=3):
return self.read_median(times) - self.get_offset_A()
def get_value_B(self, times=3):
# for channel B, we need to set_gain(32)
g = self.get_gain()
self.set_gain(32)
value = self.read_median(times) - self.get_offset_B()
self.set_gain(g)
return value
# Compatibility function, uses channel A version
def get_weight(self, times=3):
return self.get_weight_A(times)
def get_weight_A(self, times=3):
value = self.get_value_A(times)
value = value / self.REFERENCE_UNIT
return value
def get_weight_B(self, times=3):
value = self.get_value_B(times)
value = value / self.REFERENCE_UNIT_B
return value
# Sets tare for channel A for compatibility purposes
def tare(self, times=15):
return self.tare_A(times)
def tare_A(self, times=15):
# Backup REFERENCE_UNIT value
backupReferenceUnit = self.get_reference_unit_A()
self.set_reference_unit_A(1)
value = self.read_average(times)
if self.DEBUG_PRINTING:
print("Tare A value:", value)
self.set_offset_A(value)
# Restore the reference unit, now that we've got our offset.
self.set_reference_unit_A(backupReferenceUnit)
return value
def tare_B(self, times=15):
# Backup REFERENCE_UNIT value
backupReferenceUnit = self.get_reference_unit_B()
self.set_reference_unit_B(1)
# for channel B, we need to set_gain(32)
backupGain = self.get_gain()
self.set_gain(32)
value = self.read_average(times)
if self.DEBUG_PRINTING:
print("Tare B value:", value)
self.set_offset_B(value)
# Restore gain/channel/reference unit settings.
self.set_gain(backupGain)
self.set_reference_unit_B(backupReferenceUnit)
return value
def set_reading_format(self, byte_format="LSB", bit_format="MSB"):
if byte_format == "LSB":
self.byte_format = byte_format
elif byte_format == "MSB":
self.byte_format = byte_format
else:
raise ValueError("Unrecognised byte_format: \"%s\"" % byte_format)
if bit_format == "LSB":
self.bit_format = bit_format
elif bit_format == "MSB":
self.bit_format = bit_format
else:
raise ValueError("Unrecognised bitformat: \"%s\"" % bit_format)
# sets offset for channel A for compatibility reasons
def set_offset(self, offset):
self.set_offset_A(offset)
def set_offset_A(self, offset):
self.OFFSET = offset
def set_offset_B(self, offset):
self.OFFSET_B = offset
def get_offset(self):
return self.get_offset_A()
def get_offset_A(self):
return self.OFFSET
def get_offset_B(self):
return self.OFFSET_B
def set_reference_unit(self, reference_unit):
self.set_reference_unit_A(reference_unit)
def set_reference_unit_A(self, reference_unit):
# Make sure we aren't asked to use an invalid reference unit.
if reference_unit == 0:
raise ValueError("HX711::set_reference_unit_A() can't accept 0 as a reference unit!")
return
self.REFERENCE_UNIT = reference_unit
def set_reference_unit_B(self, reference_unit):
# Make sure we aren't asked to use an invalid reference unit.
if reference_unit == 0:
raise ValueError("HX711::set_reference_unit_A() can't accept 0 as a reference unit!")
return
self.REFERENCE_UNIT_B = reference_unit
def get_reference_unit(self):
return get_reference_unit_A()
def get_reference_unit_A(self):
return self.REFERENCE_UNIT
def get_reference_unit_B(self):
return self.REFERENCE_UNIT_B
def power_down(self):
# Wait for and get the Read Lock, incase another thread is already
# driving the HX711 serial interface.
self.readLock.acquire()
# Cause a rising edge on HX711 Digital Serial Clock (PD_SCK). We then
# leave it held up and wait 100 us. After 60us the HX711 should be
# powered down.
GPIO.output(self.PD_SCK, False)
GPIO.output(self.PD_SCK, True)
time.sleep(0.0001)
# Release the Read Lock, now that we've finished driving the HX711
# serial interface.
self.readLock.release()
def power_up(self):
# Wait for and get the Read Lock, incase another thread is already
# driving the HX711 serial interface.
self.readLock.acquire()
# Lower the HX711 Digital Serial Clock (PD_SCK) line.
GPIO.output(self.PD_SCK, False)
# Wait 100 us for the HX711 to power back up.
time.sleep(0.0001)
# Release the Read Lock, now that we've finished driving the HX711
# serial interface.
self.readLock.release()
# HX711 will now be defaulted to Channel A with gain of 128. If this
# isn't what client software has requested from us, take a sample and
# throw it away, so that next sample from the HX711 will be from the
# correct channel/gain.
if self.get_gain() != 128:
self.readRawBytes()
def reset(self):
self.power_down()
self.power_up()
# EOF - hx711.py